This article captures part of my team’s and my exploration and practice in international localization testing, focusing on the construction of the Prism testing platform and the technical solution for localization data testing.
Background and Challenges
In a globalized business environment, companies are paying more and more attention to the localization adaptation of their products to ensure that their products meet the needs and usage habits of users in different regions. Product localization not only involves language and cultural diversity, but also needs to consider the compatibility of technical platforms, compliance with laws and regulations, user preferences, time zones, currency management, and frequent iterative changes in content, etc. As a product quality assurance test engineer, how to provide customers with the most excellent user experience through layers of verification tests, we face a series of challenges in the process of performing localization testing:
- Resource constraints: Localization testing often requires specialized translators and test engineers. However, many companies have relatively limited resources in this area, making it difficult to ensure the quality and efficiency of testing.
- Complex scenarios: Localization testing covers multiple aspects, including translation, special character handling, currency conversion, time zone adjustment, user experience optimization, and compliance testing. These configurations and switches are often time-consuming and complex, easily leading to omissions and affecting the overall testing effect.
- Subtle differences: Users in different regions have different expectations and usage habits for products, and ensuring the accuracy of functional differences in the same version of products in different markets is a huge challenge.
- Technical integration: Currently, there are relatively few tools available on the market that can be directly used for localization testing, and they cannot fully meet our needs, requiring custom development.
Solutions
How to reduce the regression burden on testers and improve testing efficiency has become increasingly important. In addition to conventional front-end and back-end functional automated testing, facing the many pain points of localization testing has strengthened our determination to analyze and solve problems in depth. Considering the existing testing technology framework and basic capabilities, we have built the Prism testing platform, which has a simple and unified front-end operation page, provides localization data testing, multi-market push testing, and multi-language translation testing, as well as ongoing multi-time zone functional automated acceptance. In the future, we will strive to build it into a comprehensive localization testing platform for internationalization.
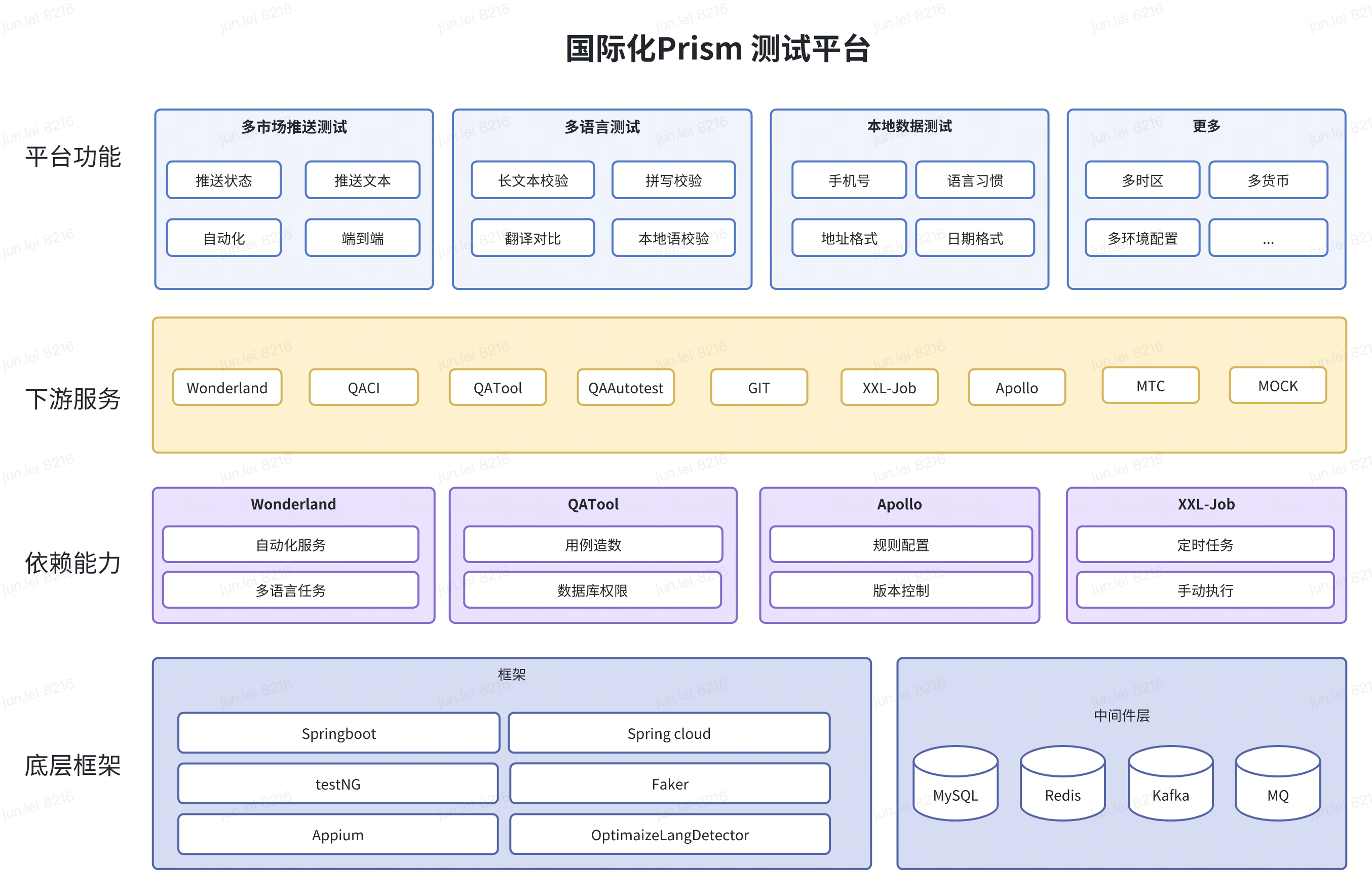
Implementation
Next, we will introduce several tools that have been implemented during the exploration of localization testing.
Localization Data Testing
With the acceleration of our company’s globalization process, testing of data text types has become increasingly diverse. Whether it is traditional UI automation or interface automation testing, the cost of discovering unknown data defects has become higher and higher. How to efficiently and accurately verify the compatibility of multi-market data has become an urgent problem to be solved. This section introduces a practical data generation technical solution that leverages the company’s MTC UI automation and QACI interface automation capabilities to automatically detect potential multi-market data compatibility defects, injecting new vitality into automated testing.
Data Prototype Collection
- User feedback: Through user research questionnaires, online feedback systems, customer service hotlines, and other channels, we have collected user feedback from different countries and regions, which are data issues and suggestions encountered by users in actual use, such as input names, addresses, contact information, etc. This feedback often directly reflects the user’s real needs and pain points.
- Market research: By utilizing data reports and industry analysis reports from market research agencies, we can understand market trends, competitors’ data processing methods, and user preferences. This helps us build a data prototype library that is more in line with market demands.
- Known defects: We have sorted out common defect data types from historical testing records, such as input methods, format errors, character parsing, language mismatches, etc. These defect types can serve as important references for building the data prototype library.

Requirement Analysis
Based on the product’s functional modules and business processes, we further determine the types of languages and text that we need to test. First, we design and construct text data in different languages, such as English, Traditional Chinese, Thai, Vietnamese, etc., targeting our existing overseas markets. At the same time, we also need to consider different styles of text expression. This test data will be used to verify the APP’s text processing capabilities and user experience in different language environments, thereby discovering potential data processing errors and boundary condition issues.
Tool Selection
We have selected the mainstream multi-language testing data tool library Faker currently available on the market. Recently, the famous mid-laner Faker from the LOL League of Legends led SKT to win the fifth championship in team history at the S14 Global Finals, making him a legend in the esports industry. Similarly, the Faker library in the IT industry is also outstanding. This tool library can provide us with rich language resources and syntax rules to help us generate test data that meets the requirements. We also found that the Faker library supports most mainstream countries and regions and languages worldwide, with field designs that reflect local language styles, such as street names, postal codes, etc.
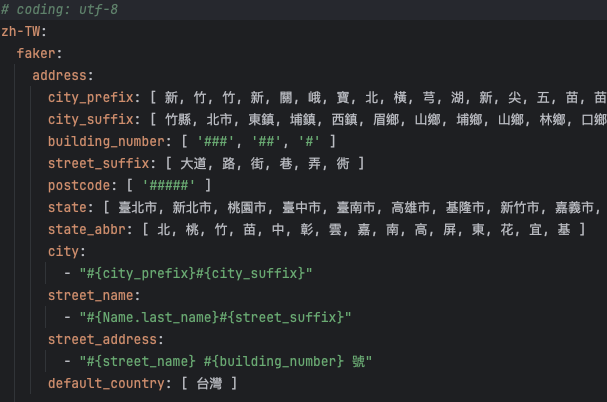
In addition to having rich language resources, Faker also has the ability to randomly generate test data, ensuring that the data scenarios we validate are different each time we run the automation pipeline, thus guaranteeing the diversity of testing and exploring more potential defects.
Data Construction
In the process of secondary development design and construction of multi-language test data, we first considered the basic core text input types for Lalamove users and drivers, such as surname, first name, full name combination, address, email, phone number, etc.
| |
Secondly, we also took into account that the formats of identity cards or passport IDs in different countries are different, so we also made customized designs for this. The Faker library provides three useful solutions for such alphanumeric combinations, namely Letterify, Numberify, and Bothify. First, Letterify helps to generate random letter sequences; while Numerify only generates numeric sequences; finally, Bothify is a combination of the two, which can create random alphanumeric sequences that can be used to simulate ID strings and other content.
FakeValueService requires a valid Locale and RandomService:
| |
In this code snippet, we create a new FakeValueService with the locale en-GB and use the bothify method to generate a unique fake ID. It works by replacing “?” with random letters and “#” with random numbers.
Similarly, regexify generates a random sequence based on a selected regular expression pattern. In this unit test code snippet, we will use FakeValueService to create a random sequence that follows a specified regular expression:
| |
Our code creates a lowercase alphanumeric string of length 10, and our pattern checks the resulting string against a regular expression.
Interaction Design
- Transmission efficiency: We use efficient data transmission protocols and compression algorithms, and optimize the data transmission process and network environment to ensure that data can be transmitted to the target platform in a timely and accurate manner.
- Transmission security: When performing UI automation testing, test data needs to be transmitted from the Prism platform to the cloud testing platform. In order to ensure the security and efficiency of data transmission, we use the HTTPS protocol for encrypted transmission and set a reasonable transmission interval and retry mechanism. This not only protects the confidentiality of the data, but also ensures that the data can reach the target platform in a timely manner, providing solid data support for the testing process.
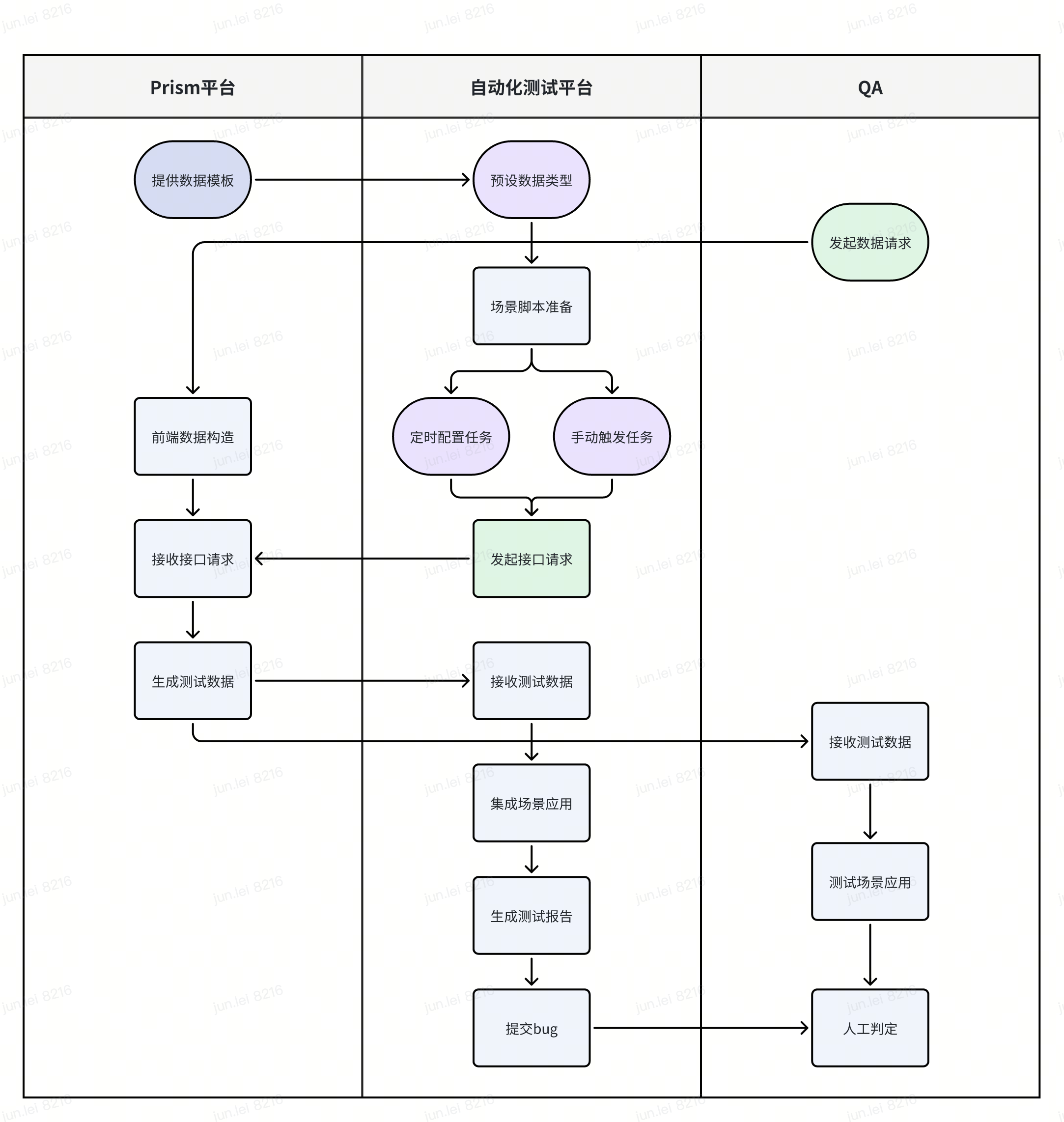
- Process analysis:
- Prism platform: provides pre-designed data templates for the automation platform and provides a friendly front-end operation interface for testers. When receiving a data construction request, the Prism platform begins to construct and generate the required data according to the requirements, and returns it to the automation platform or testers for use.
- Automated testing platform: includes mobile cloud testing platform and interface automated testing platform. First, preset the data type according to the data template provided by the Prism platform, and prepare the required automation scenario script. Next, no matter it is a scheduled task that we configure every day or a manually triggered task, as long as it hits the preset multilingual data scenario, it will automatically initiate an interface request to the Prism platform. After receiving the test data generated by Prism, it will automatically integrate the data into our application scenario and present the results in the test report.
- QA: Similarly, testers can use the Prism platform to construct test data during business testing and apply it to their own scenario verification.
- Automated integration
- Data integration solutions: For UI automation and interface automation testing, we have designed standardized data integration solutions. By utilizing data factory tools that have broken down the barriers between upstream and downstream services, we can inject test data into both the UI interface and API endpoints, achieving seamless integration and automated processing of test data.
- Intelligence: During the data integration process, we also introduced intelligent technologies to optimize data processing workflows. For example, we use machine learning algorithms to automatically classify and predict test data, enabling more accurate identification and handling of potential issues.
Assertions and Result Presentation
- Assertion rules: Based on the expected results of multilingual text on the client side and end-to-end interfaces, we have designed detailed assertion rules. These rules cover multiple aspects, including text content, format, special symbols, etc., to ensure the comprehensiveness and accuracy of test results. For example, for text content, we require the test data to match the expected results exactly; for format and special symbols, we require the test data to conform to specific specifications and standards.
- Case: In daily UI automation pipeline tasks, it is necessary to verify whether the text data entered by users in the chat dialog with drivers can be displayed correctly on the page. To achieve this, we have designed corresponding assertion rules to check the consistency of text content, format, and symbols. If the test data does not match the expected results, we will trigger an assertion failure and generate a corresponding error report.
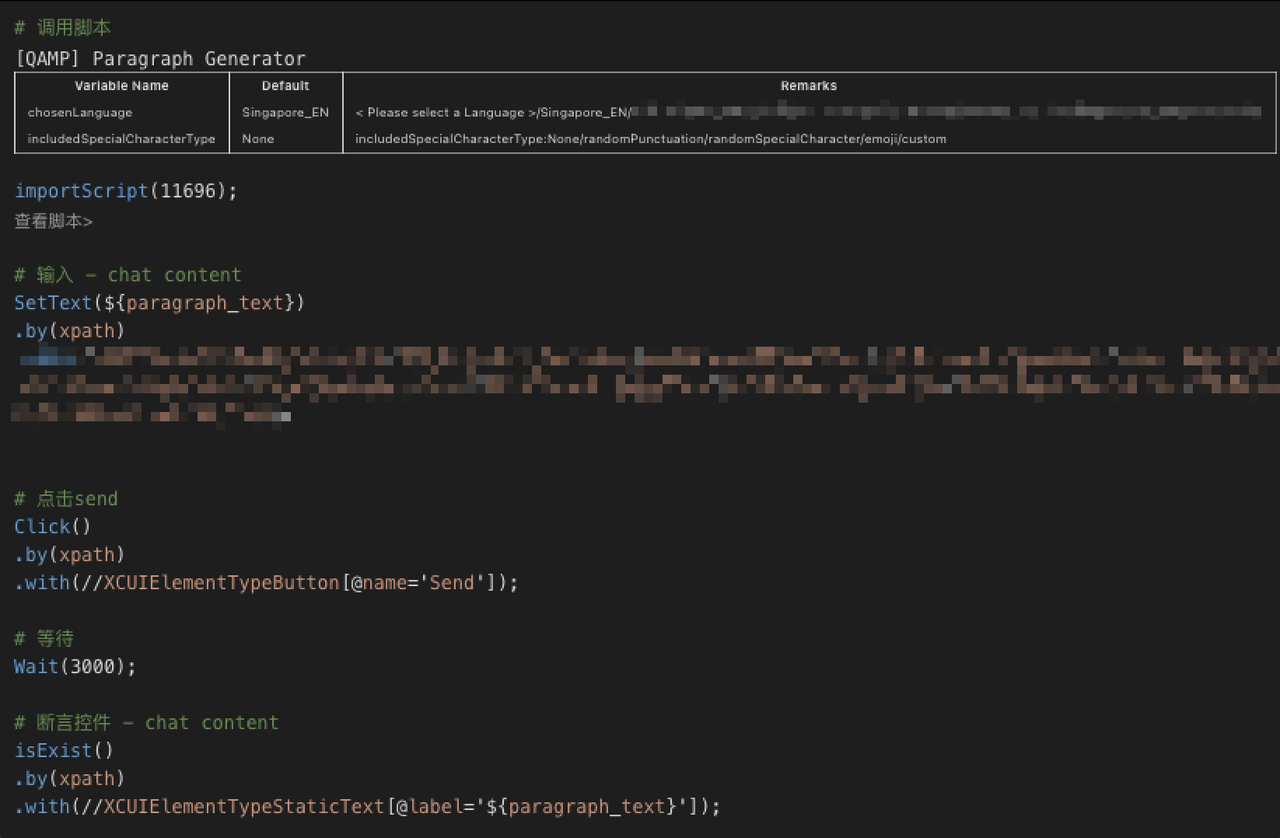
Results Presentation
- Intuitive presentation: Through the testing report system of the automation platform, we present the assertion comparison results in an intuitive and clear manner. These reports include detailed information about the test data, descriptions of the assertion rules, test results, error messages, and more. Users can quickly locate potential issues based on the information in the report, providing strong support for subsequent remediation efforts.
- Visual analysis: In order to more intuitively display test results and trends, we have also introduced visual analysis techniques. By utilizing charts and graphs to showcase the distribution of test data, types and quantities of defects, etc., we help users better understand and analyze test results.
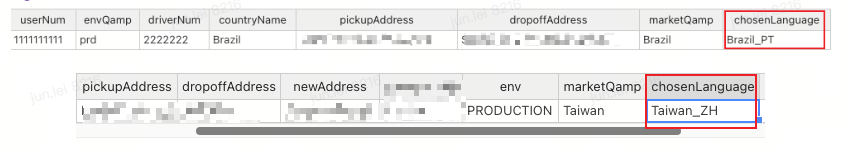
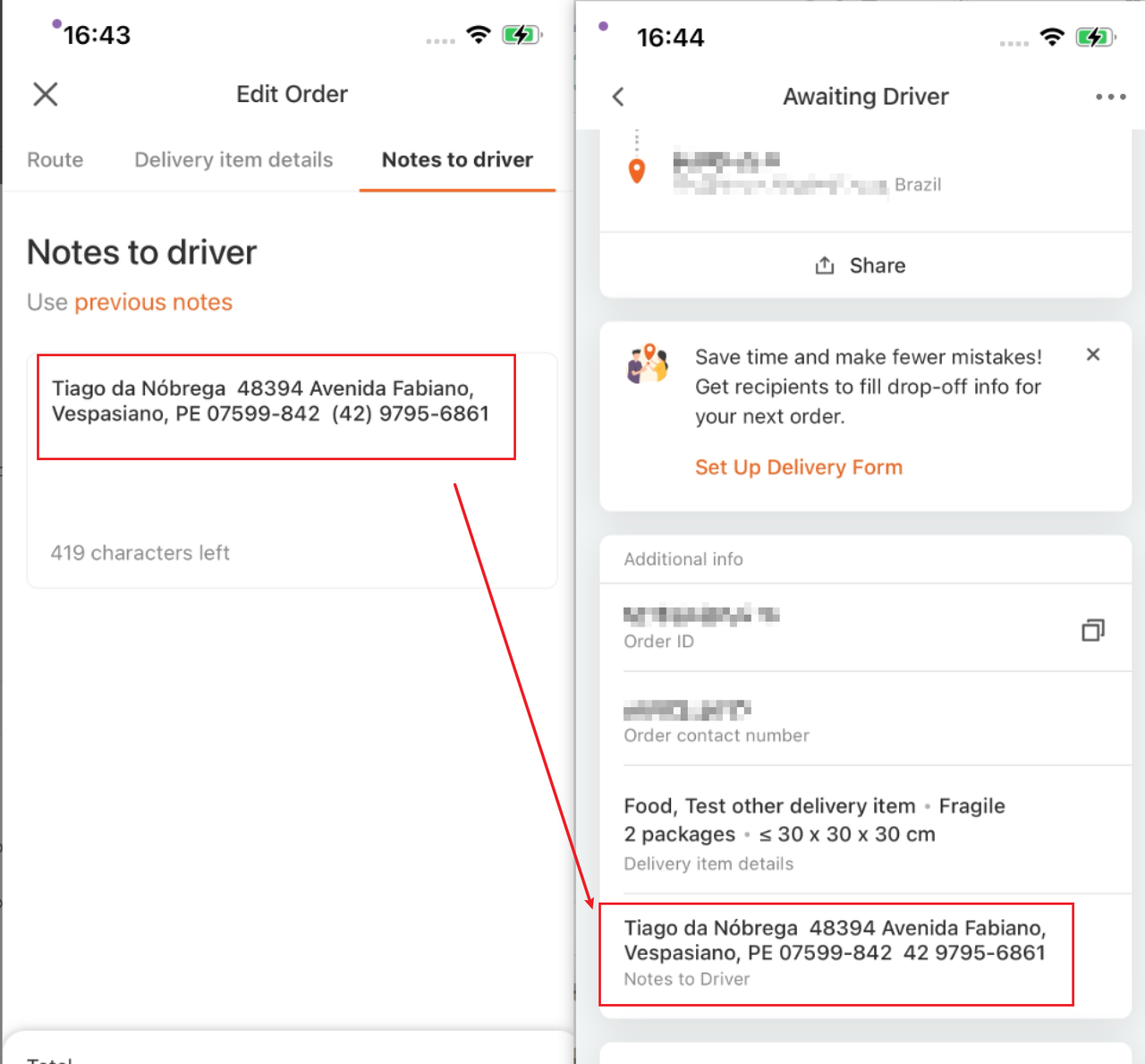
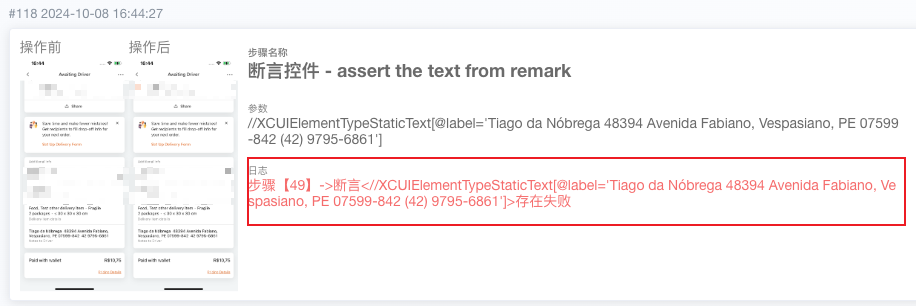
- Case: After completing a round of UI automation testing for the Brazilian market regression verification, the cloud testing platform automatically generated the corresponding test report and indicated that there was an error. The report intuitively presented the test data, assertion rules, test results, and error messages. By browsing the report, we can quickly locate the issue: in the scenario of simulating a Brazilian user sending a message to the driver, it was found that the parentheses around the phone number on the waiting driver page were missing. This shows that the automated platform, which integrates localized data detection, can replace manual testing to identify more detailed text usage defects.
References
[1]: JueJin - New Exploration of Internationalization and Localization Testing
[2]: TesterHome - New Exploration of Internationalization and Localization Testing
[3]: Faker Official Documentation
